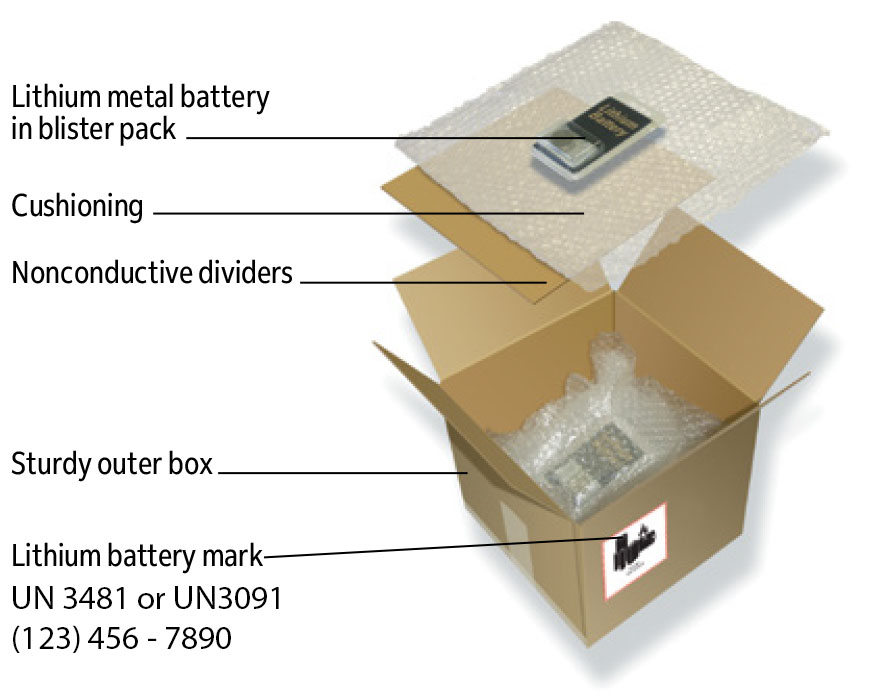
Battery Packaging Standards: Ensuring Safety, Performance, and Compliance
Battery packaging is often overlooked compared to battery capacity or lifespan. However, packaging plays a critical role in safety, performance preservation, and regulatory compliance. From lithium-ion cells powering smartphones to lead-acid batteries in vehicles and solar storage units, packaging directly affects product reliability and transportation safety.
This guide provides a complete overview of battery packaging rules, materials, and best practices, covering lithium-ion, lead-acid, alkaline, solar, and automotive batteries.
Part 1. Why Battery Packaging Matters
1. Safety Protection
Battery packaging is the final layer of defense against hazards such as:
- Thermal runaway: Prevents fires in lithium-ion batteries
- Leakage containment: Especially important for lead-acid batteries
- Short-circuit prevention: Keeps terminals isolated during transport
- Impact resistance: Minimizes damage during drops or vibrations
2. Performance Preservation
Proper packaging shields batteries from:
- Humidity that causes corrosion
- Temperature extremes that accelerate degradation
- Mechanical stress during shipping and handling
- Air pressure changes in air freight
3. Regulatory Compliance
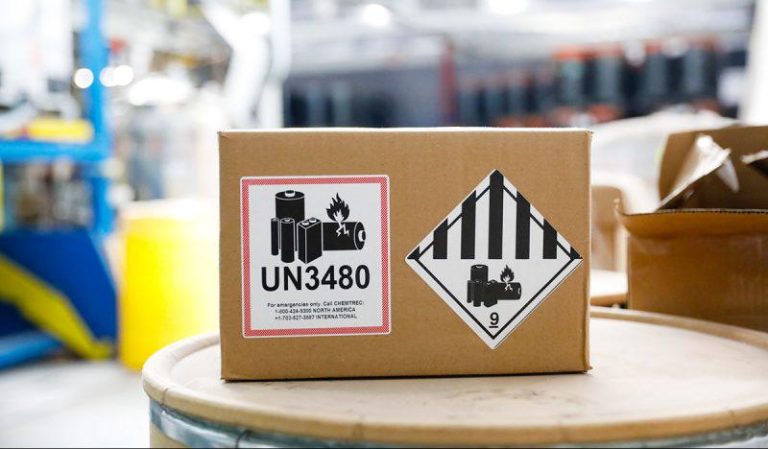
Battery shipments must comply with global standards, including:
| Battery Type | Key Regulations | Packaging Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium-ion | UN38.3, IATA DGR | Fire-resistant, drop-tested, insulated |
| Lead-acid | DOT, ADR | Acid-proof secondary containment |
| Alkaline | Non-hazardous (usually) | Moisture-resistant, tamper-proof packaging |
| Solar & EV Batteries | IEC, IMDG, IATA DGR | Weatherproof, fireproof, and modular design options |
Part 2. Battery Packaging Regulations and Testing
UN Packaging Tests for Dangerous Goods
Packaging for hazardous materials, including lithium batteries, must pass:
- Vibration Testing: Simulates road conditions
- 1.2m Drop Test: Ensures impact resistance
- Stack Test: Verifies compression strength
- Pressure Differential Test: Mandatory for air transport
Regional Variations to Note
- EU: Full supply chain traceability required
- USA (DOT, PHMSA): Focuses on hazardous materials accident prevention
- China (GB Standards): Mandates recyclability and eco-compliance
Part 3. Common Battery Packaging Materials
- Plastic casings: For consumer electronics batteries
- Aluminum shells: Provide heat resistance for high-power cells
- Cardboard boxes: For retail distribution and bulk shipments
- Fireproof pouches & metal containers: For lithium-based and EV batteries
- Moisture-proof films: For alkaline and zinc-carbon batteries
Part 4. Lithium Battery Packaging Solutions
Lithium-ion batteries are sensitive to temperature, puncture, and impact risks, requiring the most stringent packaging controls:
- Plastic Casing: Light-duty for small electronics batteries
- Aluminum Enclosures: Used in laptops, power banks, and drones
- Fireproof Pouches: For EV and e-bike batteries with high energy density
- Shock-Resistant Boxes & Foam Inserts: Protect against transit damage
Part 5. Rechargeable Battery Packaging
Rechargeable batteries (Li-ion, LiPo, NiMH, lead-acid) need packaging designed for multiple cycles of use, storage, and transportation:
- LiPo Batteries: Sealed in flexible pouches to prevent expansion leaks
- NiMH Batteries: Packaged in heat-resistant shells or metal housings
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Thick polypropylene casings to contain liquid electrolytes and vent gases
Part 6. Non-Rechargeable Battery Packaging
Primary batteries (alkaline, zinc-carbon, lithium primary) require:
- Tamper-resistant blister packs for retail safety
- Leak-proof sealed containers for transportation
- Eco-friendly recyclable cardboard to reduce environmental impact
Part 7. Solar Battery Packaging
Solar batteries face harsh outdoor conditions and must be protected against:
- UV exposure
- Temperature swings (-30°C to +60°C)
- Moisture and rodents
Typical features include:
- Weatherproof enclosures for outdoor storage
- Insulated housings for temperature control
- Fireproof cases for high-capacity LiFePO4 batteries
Part 8. Off-Grid Solar Systems
Off-grid solar battery systems often use:
- Modular battery packs for easy scalability
- Integrated Battery Management Systems (BMS) for safety control
- Heavy-duty casings for environmental protection and long service life
Part 9. Alkaline Battery Packaging
Household alkaline batteries use:
- Retail blister packs for small quantities
- Bulk cartons for industrial users
- Recyclable packaging materials for eco-compliance
Part 10. Automotive & EV Battery Packaging
- Lead-Acid Car Batteries: Packaged in vented, acid-resistant housings
- Lithium EV Batteries: Require shockproof, fireproof, temperature-controlled packaging
- Hybrid Systems: Use modular packs for easy maintenance and recycling
Part 11. Best Practices for Battery Packaging
- Use UN-Certified Packaging: Required for dangerous goods shipments
- Label Clearly: Include UN numbers, handling warnings, and orientation arrows
- Separate Terminals: Prevents short-circuits during transit
- Fireproof Materials for Lithium Batteries: Required by IATA DGR and UN38.3
- Temperature Control: Especially for solar and EV battery packs
Part 12. FAQs on Battery Packaging
Q1: What is the safest way to package lithium-ion batteries?
Use fireproof, insulated, and shock-resistant containers tested under UN38.3 and IATA DGR guidelines.
Q2: Can packaging affect battery performance?
Yes. Poor insulation or exposure to humidity and temperature extremes can degrade capacity and shorten lifespan.
Q3: Are there eco-friendly packaging options?
Yes. Recyclable cardboard, biodegradable plastics, and reusable metal casings are gaining adoption.
Q4: What about shipping damaged or defective batteries?
Damaged batteries require special UN-approved containers, hazard labeling, and carrier pre-approval.
Conclusion
Battery packaging is not just a logistics requirement—it’s a safety, compliance, and performance imperative. Manufacturers, distributors, and end-users must adopt regulation-compliant, eco-friendly, and application-specific packaging to ensure safe handling, storage, and transport.
When designed properly, packaging prevents accidents, extends battery life, and supports regulatory compliance across global supply chains.


