Battery Certification: Complete Guide to Standards, Costs, and Timelines (2025 Edition)
Battery certification is essential for ensuring the safety, performance, and regulatory compliance of battery products across industries such as energy storage, electric vehicles, consumer electronics, and industrial power systems.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the types of certifications, cost structures, timeframes, and global standards manufacturers must understand to bring battery products to market safely and legally.
Key Takeaways
- ✅ 6 Must-Have Certifications: UL, IEC, CE, UN38.3, KC, PSE
- 💵 Cost Range: $2,000 – $20,000 per certification
- ⏳ Certification Timeline: 4–12 weeks depending on battery type and region
- 🌍 Global Coverage: US, EU, Japan, South Korea, International CB Scheme
- ⚠️ Critical Risk: 30% of batteries fail initial UN38.3 altitude simulation testing
1. What is Battery Certification?
Battery certification involves testing, documentation, and third-party evaluation to verify compliance with safety, performance, and environmental standards.
Benefits include:
- Safety Assurance: Mitigates risks of fire, explosion, or leakage.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meets legal requirements for specific markets.
- Market Access: Required for product entry into the EU, US, Japan, Korea, and beyond.
- Consumer Confidence: Certifies reliability and quality for end-users.
2. Top 10 Battery Certifications for Global Markets
Depending on battery chemistry, application, and target markets, the following certifications are most commonly required:
| Certification | Scope / Application | Key Standards & Notes |
|---|---|---|
| UL Certification | US safety standard for cells, packs, ESS | UL 1642 (cells), UL 2054 (packs), UL 1973 (stationary) |
| IEC Certification | International standards for safety/performance | IEC 62133 (portable), IEC 62619 (EV batteries) |
| CE Marking | EU market access requirement | Covers safety, EMC, RoHS, Battery Directive |
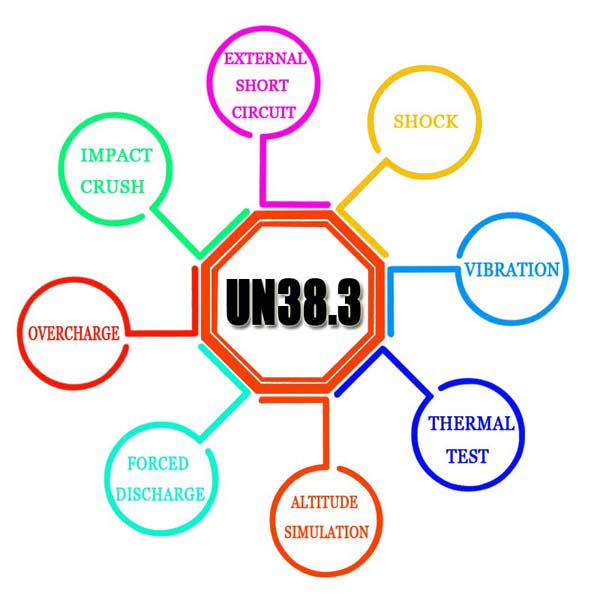
| UN38.3 Certification | Lithium battery transportation safety | Required for IATA/IMDG air/sea shipment approval |
| ISO Certifications | Quality & environmental management | ISO 9001, ISO 14001 compliance |
| KC Certification | South Korea regulatory compliance | Mandatory for batteries sold in Korea |
| CB Scheme | Multi-country certification pathway | Harmonizes IEC test reports for global acceptance |
| PSE Certification | Japan safety approval for electrical products | Mandatory for lithium-ion batteries |
| RoHS Compliance | EU hazardous substances restriction | Limits lead, mercury, cadmium, and other toxic materials |
| MSDS (Documentation) | Safety data sheets for materials & chemicals | Required for shipping, handling, and workplace safety |
3. Battery Certification Costs (2025 Estimates)
| Certification | Typical Cost (USD) | Notes on Cost Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| UL Certification | $15,000 – $20,000 | Complex packs require more tests |
| IEC Certification | $6,000 – $10,000 | Cell vs. pack scope impacts cost |
| CE Marking | $2,000 – $5,000 | Self-declaration possible <100Wh |
| UN38.3 Certification | $5,000 – $7,000 | Includes 1.2m drop & altitude tests |
| KC Certification | $3,000 – $5,000 | Korea market access requirement |
| CB Scheme | $4,000 – $6,000 | Single test for multiple markets |
| PSE Certification | $2,000 – $4,000 | Required in Japan for batteries |
Costs depend on battery chemistry, design complexity, and testing lab rates.
4. Certification Timelines
| Certification | Typical Duration | Key Factors Impacting Time |
|---|---|---|
| UL Certification | 10–12 weeks | Pack size, energy rating, design |
| IEC Certification | 6–8 weeks | Chemistry, cycle life tests |
| CE Marking | 2–6 weeks (self-declare) | Notified Body adds 4–8 weeks |
| UN38.3 Certification | 4–6 weeks | Shipping & transport safety tests |
| KC Certification | 4–8 weeks | Korean regulatory process |
| CB Scheme | 6–10 weeks | Multi-country harmonization |
| PSE Certification | 4–6 weeks | Japan-specific safety standards |
5. Key Battery Standards
- Safety Standards
- UL 1642: Lithium cell safety (fire & explosion prevention)
- IEC 62133: Portable secondary cell safety requirements
- Performance Standards
- UL 2054: Battery pack performance & endurance
- IEC 61960: Lithium battery performance specifications
- Environmental Standards
- ISO 14001: Environmental management across battery lifecycle
6. Battery Certification Process
- Pre-Certification Assessment – Determine required markets & standards.
- Sample Preparation – Produce test-ready battery prototypes.
- Testing & Evaluation – Conduct mechanical, electrical, thermal, and transport safety tests.
- Technical Documentation – MSDS, schematics, risk assessments, QC documentation.
- Certification Issuance – Receive official certificates upon passing tests.
- Ongoing Compliance – Annual audits and recertification after design changes.
7. Common Challenges in Battery Certification
- Regulatory Complexity: Different standards across markets increase cost & time.
- High Failure Rates: 30% fail UN38.3 altitude tests due to poor pressure design.
- Documentation Errors: Missing MSDS, circuit diagrams, or ISO records delay approvals.
- Transport Restrictions: Air & sea shipment approvals require IATA/IMDG compliance.
8. 5 Critical Mistakes to Avoid
- Using uncertified cells from suppliers without traceable quality documentation.
- Ignoring EU 2024 Battery Directive carbon footprint labeling requirements.
- Underestimating UN38.3 altitude simulation requirements (>15,000m tests).
- Submitting incomplete technical files lacking MSDS or ISO 9001 QC documents.
- Neglecting IATA/IMDG transport approvals for certified batteries.
9. FAQs
Q1: How long does certification take?
Full certification for lithium batteries typically requires 3–6 months.
Q2: What is the cheapest certification?
UN38.3 transport certification ($2,500–$5,000) is the lowest-cost requirement.
Q3: Is CE certification valid across Europe?
Yes, across all 27 EU member states; Germany may require additional GS markings.
Q4: Can manufacturers self-certify CE compliance?
Yes, for batteries <100Wh capacity; larger batteries require Notified Body testing.
Q5: How long is certification valid?
UL, IEC: 3–5 years; UN38.3: re-testing required after any design modification.
10. Conclusion
For manufacturers like inntbattery, battery certification is not optional—it is essential for safety, compliance, and global market access. By understanding costs,