Exploring Battery Drop Testing: What You Need to Know
Battery drop testing is a critical method used to evaluate the durability and safety of battery products under realistic handling conditions. In this procedure, batteries are intentionally dropped in controlled ways to simulate impacts that may occur during transport, installation, or everyday use. By studying how batteries respond to these drops, manufacturers can identify potential weaknesses in cell construction, pack design, and packaging.
Understanding battery drop test procedures, test types, applicable standards, and regulatory expectations is essential for ensuring product quality, reducing field failures, and maintaining compliance in global markets. In the following sections, we will examine why drop tests are important, how they are performed, and how they influence overall battery safety and performance.
Part 1. What is a battery drop test?
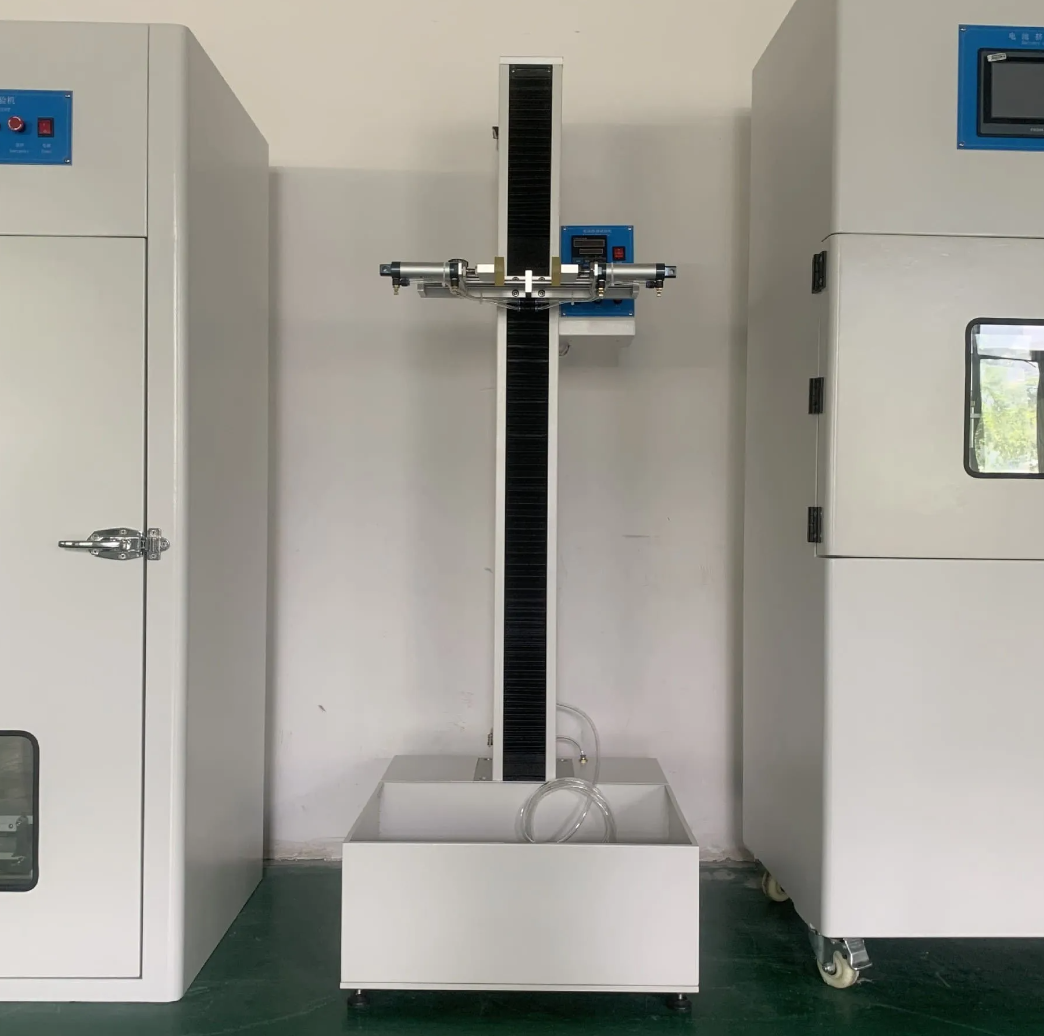
A battery drop test is a controlled impact test used to evaluate how well a battery or battery pack withstands drops that can occur in real-world use, handling, and transportation. By dropping batteries from specified heights and orientations, engineers can identify design weaknesses, verify safety, and confirm that products meet relevant standards and customer expectations.
Battery drop testing is especially important for lithium batteries, since mechanical damage can lead to internal short circuits, leakage, thermal events, or loss of performance.
Main purposes of battery drop testing
Identification of weaknesses
Drop tests help reveal weak points in cell construction, pack housing, and packaging. Typical issues include cracked housings, displaced cells, damaged welds, or insufficient internal cushioning. Identifying these problems early allows manufacturers to reinforce the design before mass production.
Safety evaluation
By subjecting batteries to impact loads, manufacturers can evaluate the risk of leakage, venting, thermal runaway, or fire. The goal is to confirm that batteries remain safe after drops within the defined test conditions and comply with applicable safety standards and regulations.
Quality assurance
Integrating drop tests into routine quality assurance ensures that every production batch can withstand handling and transport without compromising performance or safety. This reduces field failures, warranty returns, and safety incidents.
Customer satisfaction
Batteries that survive realistic drop conditions without visible damage or performance loss provide a better user experience. Reliable products increase customer confidence, support positive reviews, and strengthen brand loyalty.
Regulatory and standard compliance
Many industries and application standards include mechanical impact or drop test requirements. Drop testing helps manufacturers demonstrate compliance with these standards and with transport-related regulations, which builds trust with regulators, customers, and other stakeholders.
Part 2. Battery drop test procedure
Although details vary by standard and application, most battery drop tests follow a similar sequence. A clear, repeatable procedure is essential for meaningful results.
Pre-test preparation
- Inspect batteries
Check each battery or pack for pre-existing defects, deformation, or damage. Only undamaged samples should be used for the drop test. - Set state of charge
Charge or discharge the batteries to the required state of charge specified by the test standard or internal test plan, for example full charge or a defined partial charge. - Prepare packaging, if applicable
If the test is intended to evaluate packaged products, place the batteries in their normal sales or transport packaging according to the test requirements. - Label samples
Assign identification numbers or codes to each sample so that test results, photos, and observations can be traced back to the correct unit.
Test setup
- Testing environment
Conduct the test in a controlled area with adequate safety precautions, good lighting, and a stable, flat impact surface. - Equipment
Use a suitable drop test apparatus that allows accurate control of drop height and orientation. The impact surface is typically a rigid, impact-resistant material such as steel or concrete, as defined by the applicable standard. - Orientation
Position the battery or packaged product in the required orientation, for example flat face, edge, or corner. Different standards specify different combinations of impact positions. - Drop height
Set the drop height according to the relevant standard or customer requirement. For many portable devices this may be around 1 meter, while other applications can require different heights.
Drop test execution and evaluation
- Perform the drop
Release the battery or package from the specified height, ensuring a free fall without interference so that the impact is clean and repeatable. - Repeat drops
Perform the required number of drops, often multiple impacts from different orientations. Some procedures require several drops on the same sample, while others use fresh samples for each orientation. - Record test conditions
Document drop height, orientation, impact surface, sample ID, ambient temperature, and any other relevant parameters for each drop. - Inspect and document results
After each drop, inspect the battery or package for visible damage, deformation, leakage, venting, unusual odor, or functional failure. Record all observations in detail and, where appropriate, measure post-test performance such as capacity or internal resistance. - Post-test analysis
Review all collected data and compare the results with acceptance criteria defined in the applicable standard or customer specification. If failures occur, use the findings to drive design improvements in the battery, housing, or packaging.
Part 3. Types of Battery Drop Tests
Battery drop testing can be tailored to different use cases and environments. In practice, manufacturers often combine several types of drop evaluations to build a complete picture of mechanical robustness and safety.
Mechanical Drop Test
Definition
Mechanical drop tests evaluate the physical durability of a battery or battery pack by dropping it from specified heights onto a rigid surface. This is the most common and fundamental form of drop testing.
Variations
Batteries may be dropped in multiple orientations, for example:
- Flat face
- Edge
- Corner
Each orientation stresses different parts of the housing and internal structure, helping uncover weaknesses that may not appear under a single impact direction.
Impact Surfaces
Typical impact surfaces include steel, concrete, or hard-engineered plates. These surfaces simulate real-world impacts that can occur during handling, warehouse operations, or transport incidents.
Impact Analysis
After each drop, the battery is inspected for:
- Cracks or deformation of the casing
- Cell displacement or internal damage
- Signs of leakage, venting, or internal short circuit
The goal is to verify that the battery remains safe and structurally sound after realistic mechanical abuse.
Thermal Drop Test
Definition
Thermal drop tests evaluate how batteries behave when drops occur at elevated or reduced temperatures.
Procedure
Before dropping, batteries are conditioned at defined temperatures, for example:
- High temperature for hot-climate or under-hood conditions
- Low temperature for cold-chain or outdoor applications
Once stabilized at the target temperature, the batteries are subjected to drop impacts according to the test plan.
Significance
This type of testing is important for applications in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, outdoor equipment, and industrial systems, where batteries must remain safe and functional under extreme temperature conditions.
Performance Metrics
Evaluations focus on:
- Integrity of the housing and seals after impacts at temperature
- Maintenance of electrical performance within acceptable limits
- Absence of hazardous behavior such as leakage, venting, or thermal events
Environmental Drop Test
Definition
Environmental drop tests combine drop impacts with environmental stresses such as humidity and pressure changes. They are designed to verify that batteries can withstand real-world logistics and operating environments.
Humidity Variations
Batteries may be exposed to high or low humidity conditions before drop testing. This helps evaluate:
- Seal integrity
- Resistance to moisture ingress
- Potential corrosion of terminals or metal parts
Altitude Considerations
Simulated high-altitude or low-pressure environments can be combined with drop tests, reflecting conditions that may occur in air transport or high-altitude deployments.
Resilience Assessment
The objective is to confirm that batteries remain safe and functional across a range of climates and operating environments, from humid coastal regions to dry or high-altitude locations.
Part 4. Battery Drop Test Standards and Regulations
International Standards
Several international standards include mechanical impact or drop-related requirements for batteries, contributing to overall safety and reliability.
IEC Standards
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) publishes widely used standards for rechargeable cells and batteries.
- IEC 62133 includes mechanical tests for portable rechargeable cells and battery packs, such as free-fall or impact tests, to evaluate safety under handling conditions.
- Other IEC standards, for example IEC 62619 or application-specific documents, may include mechanical robustness requirements for industrial and energy storage batteries.
UN and Transport-Related Requirements
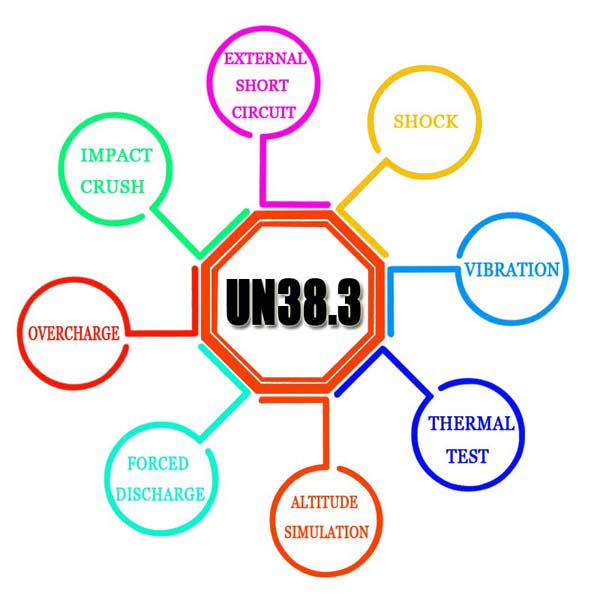
For lithium batteries used in transport, UN 38.3 is a key reference for safety under logistics conditions. While it focuses on transport-related tests such as altitude, thermal cycling, vibration, mechanical shock, external short circuit and forced discharge, it is often used together with packaging performance tests that include drop evaluation.
In automotive and other high-demand sectors, additional standards may apply, such as ISO-based traction battery test standards or OEM-specific specifications, which include various mechanical impact and abuse tests.
Application and Compliance
Different industries, such as consumer electronics, automotive, industrial equipment and aerospace, typically reference a combination of IEC, UN and industry-specific standards. Aligning drop tests with the correct standards ensures that batteries perform safely in their intended applications and helps reduce the risk of field failures.
Regulatory Compliance
Importance
Regulatory frameworks often incorporate or reference international standards. Compliance helps manufacturers demonstrate that batteries can withstand mechanical impacts and other stresses encountered in transport and use.
Safety Assurance
Requirements derived from UN transport recommendations and modal regulations (such as IATA DGR for air and the IMDG Code for sea) are designed to prevent accidents caused by damaged or improperly packaged batteries. Mechanical robustness, including resistance to drops, is an essential part of this safety strategy.
Certification
Many markets require proof of compliance from accredited third-party laboratories. Test reports and certificates are frequently necessary for customs clearance, carrier acceptance and market access.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failure to meet applicable standards and regulations may lead to:
- Product recalls or shipment rejections
- Financial penalties and legal exposure
- Damage to brand reputation
- Increased risk of safety incidents, including fire or explosion
Performing well-designed drop tests as part of a broader compliance program helps mitigate these risks.
Part 5. FAQs
What types of batteries are subject to drop testing?
Drop testing is widely applied to many battery types, including lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride, nickel-cadmium and alkaline batteries. The exact test conditions depend on the battery’s application, size, enclosure design and the standards or regulations that apply in the target market.
How often should battery drop tests be conducted?
Drop tests should be carried out during the development of new designs, whenever there are significant changes to materials, structure or packaging, and as part of periodic quality validation on production units. Regular testing ensures that design robustness is maintained over time, not only in early prototypes.
What happens if a battery fails the drop test?
If a battery does not meet the acceptance criteria, engineers should perform a detailed failure analysis to identify the root cause. Possible actions include reinforcing the enclosure, improving internal cushioning or cell fixation, adjusting welds and interconnects, or upgrading packaging design. New samples must then be tested again to confirm that the design changes have resolved the issue.
Can drop testing damage the battery permanently?
Yes. Drop testing can cause permanent mechanical and electrical damage, including internal short circuits, loss of capacity or structural cracking. For this reason, test samples should not be returned to normal use. The purpose of the test is to understand how the product behaves under mechanical abuse and to ensure that any damage does not create unacceptable safety risks.
Are there automated systems for battery drop testing?
Yes. Automated drop test systems are commonly used in professional laboratories. They can precisely control drop height, orientation and impact location, and can repeat drops with high consistency. These systems improve the repeatability of results, reduce operator variability and support more accurate comparison between different designs or production batches.