All You Need to Know About CB Certification for Lithium Batteries
CB certification plays a key role in proving that lithium batteries meet internationally recognized safety and performance requirements. As part of the IECEE CB Scheme, it allows test reports and certificates from one member country to be accepted by many others, simplifying market access and reducing duplicate testing.
For lithium battery manufacturers, CB certification is an efficient way to show global customers and regulators that their products have been evaluated to relevant IEC standards for electrical, mechanical and thermal safety. For importers and end users, a CB-tested battery provides added assurance that it has undergone independent, standardized evaluation rather than only in-house testing.
In this article, we will explain what CB certification is, why it is particularly important for lithium batteries, how the certification process works in practice and what advantages it offers for international sales, brand credibility and regulatory compliance.
Part 1. What is CB Certification?
CB Certification is part of the IECEE CB Scheme (IEC System for Conformity Testing and Certification of Electrical and Electronic Components, Equipment and Products). It is not a single “standard” itself, but a global system that allows test reports and certificates issued to IEC standards in one member country to be accepted by other member countries.
Under the CB Scheme, recognized Certification Bodies (NCBs) and their associated CB Testing Laboratories (CBTLs) evaluate products against relevant IEC standards. When a product passes these tests, the NCB issues a CB Test Certificate and CB Test Report. Other NCBs can then use these as the technical basis for granting local approvals, significantly reducing duplicate testing.
CB Certification applies to a wide range of electrical and electronic products, including lithium batteries and battery chargers. For buyers and regulators, a CB certificate is a strong indication that the product has been independently tested against internationally recognized IEC safety requirements. For manufacturers, it is an efficient way to support global market approvals from a single test program.
Part 2. Importance of CB Certification for Lithium Batteries
- Safety and Quality Assurance
- Compliance with standards
CB Certification demonstrates that lithium batteries have been tested against relevant IEC standards, confirming compliance with defined safety and performance requirements. This typically covers electrical, mechanical and thermal safety aspects. - Confidence for the market
OEMs, importers, distributors and end users can rely on CB-tested batteries as having undergone independent evaluation instead of only in-house testing. This reduces the risk of incidents such as overheating, short circuits or fire caused by design or manufacturing defects.
- Global Market Access
- International acceptance
The CB Scheme is specifically designed to support mutual recognition. A CB Test Certificate and Report can be used to obtain national certifications in many member countries with reduced or no retesting, depending on local rules. - Easier export and fewer trade barriers
With CB Certification, lithium battery manufacturers can streamline entry into multiple markets. Many local certification bodies treat CB documentation as a primary input, which simplifies approval procedures and shortens time to market. - Stronger product reputation
The CB mark (or reference to CB reports) signals that the product is aligned with international safety expectations, which can enhance trust in the brand and drive demand from professional buyers.
Part 3. CB Certification Process for Lithium Batteries
- Application Process
- Choice of Certification Body
The manufacturer selects an IECEE-recognized National Certification Body (NCB) that supports the relevant IEC battery standards. The NCB or its associated CBTL will guide the project. - Submission of documentation
The applicant provides technical information such as:- Electrical and mechanical design details
- Circuit diagrams and BMS/protection descriptions
- Safety data sheets (SDS) for cells and packs
- Information on materials, enclosures and markings
- Existing test data, if available
- Testing and Evaluation
- Test execution
Representative lithium battery samples are sent to a CB Testing Laboratory. The laboratory performs tests according to the selected IEC standard(s) for the specific battery type and application. - Typical test categories
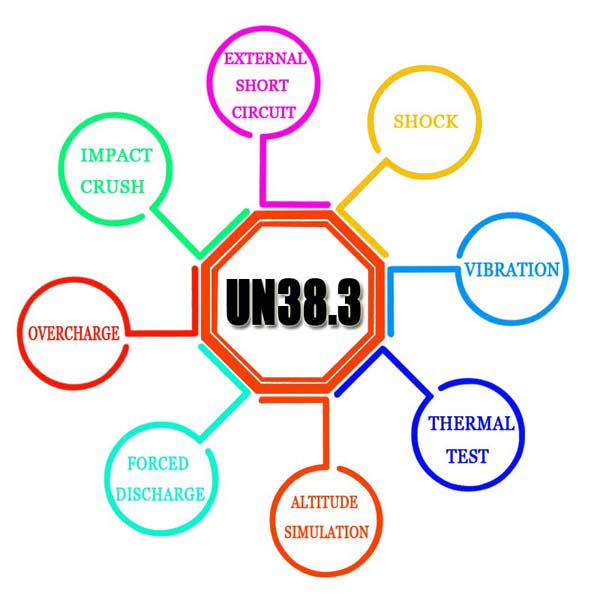
Depending on the standard, the evaluation may include:- Electrical tests: charge and discharge behavior, overcharge, short-circuit response, fault conditions
- Mechanical tests: vibration, shock, impact, crush or drop, as applicable
- Environmental tests: temperature cycling, high and low temperature operation, humidity, storage conditions
- Certification Issuance
- Review of results
The NCB reviews all test reports and documentation to confirm that the battery meets the relevant IEC requirements and that construction is consistent with the tested samples. - CB Test Certificate and Report
If the product complies, the NCB issues a CB Test Certificate accompanied by a detailed CB Test Report. These documents can then be presented to other NCBs in the CB Scheme to obtain local marks without repeating the full test program. - Ongoing validity
CB Certificates do not have a single fixed global validity period. Their practical validity depends on:- Whether the IEC standard is updated
- Whether the product design changes
- The policies of the issuing NCB and the accepting NCBs
Significant design changes or relevant standard revisions may require supplementary testing or an updated certificate.
Part 4. Benefits of CB Certification for Lithium Battery Manufacturers
Enhanced Market Access
- Global recognition
A CB Test Certificate is accepted by many certification bodies in member countries, allowing manufacturers to leverage one test program to support multiple national approvals. - Faster approvals
Because local bodies can use CB documentation as the technical basis, approval cycles are often shorter and more predictable, improving time to market.
Increased Customer Confidence
- Quality and safety signal
CB Certification tells customers that the battery has been tested according to IEC standards in an accredited laboratory. This is especially important for OEM customers integrating batteries into higher-value equipment. - Stronger brand reputation
Manufacturers with CB-certified products demonstrate that they invest in safety and compliance, which improves their position with professional buyers and long-term partners.
Competitive Advantage
- Differentiation
In tenders and B2B negotiations, CB documentation is often a key requirement. Having CB-certified batteries can be a decisive advantage over competitors with only internal or limited third-party tests. - Preferred by distributors and system integrators
Distributors, assemblers and integrators frequently prefer products supported by CB reports, as this simplifies their own product approvals and reduces risk.
Cost and Efficiency
- Reduced retesting
Instead of repeating full test programs for each country, manufacturers can use CB reports as a base and only perform additional local tests if required. This cuts testing costs and reduces project duplication. - Lower risk of non-compliance
By aligning with IEC standards early and verifying compliance through CB testing, manufacturers reduce the likelihood of failures in local approval processes, product recalls or retrofit campaigns.
Compliance and Safety
- Strong regulatory foundation
Many national regulations and certification schemes are built on IEC standards. A CB certificate provides a robust technical foundation for meeting those rules. - Improved product safety
The structured test program helps identify weaknesses in battery design, protection circuits or construction. Addressing these issues before mass production enhances safety and reduces field failures.
Part 5. What Products Does the CB Scheme Cover?
The CB Scheme covers a wide range of electrical and electronic products, many of which are closely related to lithium battery applications and ecosystems.
Electrical and Electronic Equipment
- Household appliances
Refrigerators, washing machines, microwaves, vacuum cleaners and other domestic appliances are tested for electrical safety, insulation and fire risk. - Consumer electronics
Televisions, audio systems, game consoles and similar devices are evaluated for electrical safety and, when relevant, EMC and performance-related criteria.
IT and Office Equipment
- Computers and peripherals
Desktops, laptops, monitors, printers and scanners are commonly certified under IEC IT and AV standards through the CB Scheme. - Office machines
Equipment such as copiers and multifunction devices are tested for safe operation in office environments.
Lighting Equipment
- Lamps and luminaires
From basic household luminaires to industrial fixtures, products are checked for electrical safety, thermal behavior and, where applicable, energy efficiency requirements. - LED lighting
LED lamps and drivers are evaluated for safety, reliability and proper thermal management to ensure long service life and stable performance.
Medical Devices
- Diagnostic equipment
Devices such as X-ray machines, MRI systems and ultrasound equipment are evaluated against stringent IEC medical standards for safety and essential performance. - Therapeutic equipment
Equipment such as infusion pumps and certain therapy devices may be supported by CB reports as part of their wider medical device conformity assessment.
Industrial and Energy Equipment
- Automation and control equipment
Controllers, drives, sensors and related components are tested for safety and robust operation in industrial environments. - Power tools and industrial tools
Tools such as drills, grinders and saws are assessed for electrical safety and mechanical robustness. - Solar and renewable energy products
Photovoltaic modules, inverters and some small wind and associated control equipment can be evaluated under IEC standards within the CB Scheme, supporting safe deployment of renewable energy systems.
Batteries and Chargers
- Lithium batteries
Lithium battery packs and systems used in electronics, energy storage and e-mobility can be tested to the relevant IEC standards under the CB Scheme, focusing on electrical, mechanical and thermal safety. - Battery chargers and power supplies
Chargers, external power supplies and on-board charging units are also within the scope, ensuring safe charging behavior and compliance with IEC safety standards.
Part 6. FAQs
What does “CB” stand for in CB Certification?
“CB” stands for “Certification Body.” The CB Scheme is operated by the IECEE (IEC System for Conformity Testing and Certification of Electrical and Electronic Components, Equipment and Products) and is based on mutual recognition of test results among participating certification bodies.
How long does the CB Certification process take?
The timeframe depends on product complexity, documentation quality and laboratory workload. For many products, the process can take from several weeks to a few months. Complex systems, multiple variants or significant non-conformities can extend the schedule.
Can CB Certification be used in multiple countries?
Yes. That is the main purpose of the CB Scheme. A CB Test Certificate and Report can be submitted to other NCBs within the IECEE network to obtain national marks with reduced or no additional testing, subject to each country’s rules.
Is CB Certification legally mandatory?
CB Certification itself is usually not a legal requirement. However, it is widely used as a technical basis to obtain national certifications that may be mandatory. It is strongly recommended for manufacturers targeting multiple markets, as it simplifies approvals and strengthens trust with customers.
How does CB Certification differ from CE marking?
CB Certification is a conformity assessment system based on IEC standards and recognized among participating certification bodies worldwide.
CE marking is a legal requirement within the European Economic Area that indicates conformity with EU directives and regulations (such as Low Voltage, EMC, RoHS). In many cases, CB test reports to IEC standards are used as key technical evidence to support CE conformity, but CB Certification and CE marking belong to different regulatory frameworks.