What’s UL1642 Certification?
Part 1. What is UL 1642?
UL 1642 is a safety standard developed by Underwriters Laboratories (UL) specifically for lithium cells and batteries (both primary and rechargeable) used in electronic products. It defines construction requirements and a series of abuse tests to verify that lithium cells can operate safely under normal use and reasonably foreseeable misuse, without causing fire, explosion or dangerous leakage.
Cells evaluated to UL 1642 are subjected to mechanical, electrical and thermal abuse conditions such as crush, impact, short circuit and abnormal charging. Passing these tests demonstrates that the cell’s design, materials and protection features provide an acceptable level of safety for integration into consumer, industrial, IT, medical and other types of equipment.
For manufacturers and end users, UL 1642 certification is an important signal that a lithium cell has been independently evaluated to a recognized North American safety benchmark, helping support product compliance, brand credibility and market acceptance.
Part 2. What products does UL 1642 cover?
Strictly speaking, UL 1642 applies to lithium cells and batteries used as components in products, not to all battery chemistries. Typical applications include:
Lithium primary cells
Non-rechargeable lithium cells used in products such as meters, sensors, memory backup, medical devices and industrial electronics. UL 1642 verifies that these cells can withstand defined abuse conditions without creating unsafe situations.
Lithium-ion and lithium-ion polymer cells
Rechargeable lithium cells used inside smartphones, laptops, wearables, power tools, medical equipment and many other portable devices. UL 1642 focuses on the cell level; complete packs and battery systems are usually evaluated under other UL standards (for example UL 2054, UL 2271, UL 1973), but they often rely on UL 1642–compliant cells.
Other chemistries such as NiMH, NiCd, lead-acid and alkaline are covered by different UL standards and are not within the direct scope of UL 1642. However, finished products that use multiple battery types may reference a combination of cell-level and pack-level standards during overall certification.
Part 3. What is the UL 1642 standard for lithium cells and batteries?
The UL 1642 standard sets out design and test requirements to confirm that lithium cells and batteries can be used safely as components in electronic products.
Key aspects include:
Physical construction
- Cell design and enclosure
Requirements for robust cases, seals and terminals to reduce the likelihood of mechanical damage, internal short circuit or electrolyte leakage. - Insulation and clearances
Minimum insulation distances and construction rules to minimize the risk of internal shorts or breakdown under thermal and mechanical stress.
Electrical performance
- Normal operation
Verification that cells meet their declared electrical ratings (voltage, capacity) and operate within safe limits under normal charge and discharge conditions. - Electrical abuse
Evaluation of the cell’s behavior under abnormal conditions, such as external short circuit, forced discharge or abnormal charging, to ensure it does not ignite or explode.
Environmental and mechanical testing
- Temperature, vibration and shock
Tests that assess how the cell behaves under temperature extremes, vibration and mechanical shock representative of real-world use, storage and transport.
Safety features
- Protective elements
Where applicable, evaluation of built-in safety devices (for example, current interrupt devices, PTCs, venting mechanisms) to confirm they function as intended under fault conditions.
Chemical considerations
- Electrolyte and materials
Review of materials and construction to ensure that, even if a fault occurs, the risk of fire, explosion or hazardous leakage is minimized in accordance with the standard’s criteria.
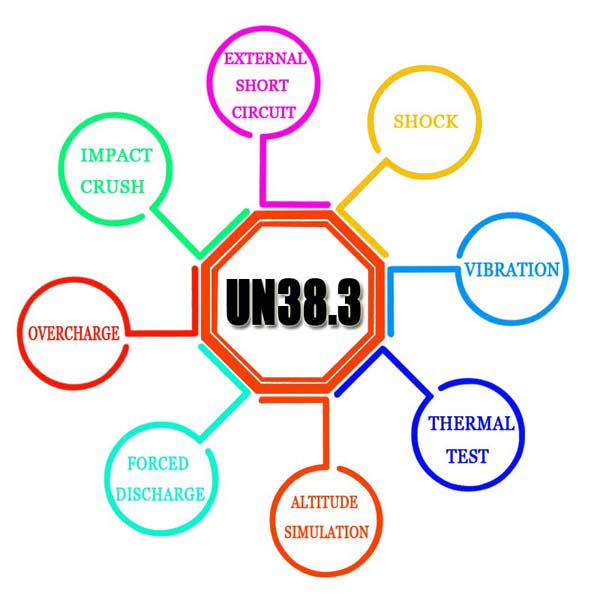
Part 4. Typical test items for UL 1642 certification
UL 1642 includes a series of abuse tests designed to challenge the safety margins of lithium cells and batteries. While exact details and applicability depend on the cell type, common test categories include:
Overcharge test
Evaluates how the cell behaves when charged beyond its specified limits. The cell must not vent violently, catch fire or explode when subjected to defined overcharge conditions.
Forced discharge / overdischarge test
Assesses the cell’s response when it is driven into deep discharge or reverse charge (for example, in a series string fault). The cell must withstand these conditions without hazardous failure.
External short circuit test
Simulates an external short across the cell terminals. The test checks that the cell’s design and protective features limit temperature rise and prevent fire or explosion.
Crush test
Applies a controlled mechanical force to the cell to simulate severe mechanical abuse. The cell must not rupture violently or ignite under the specified crush conditions.
Impact test
Subjects the cell to a defined impact (for example, a weight dropped from a specified height) to evaluate its resistance to mechanical shocks and deformation.
Temperature cycling / thermal test
Exposes the cell to repeated cycles of high and low temperatures to verify its stability and safety under thermal stress and changing environmental conditions.
Vibration and mechanical shock tests
Simulate vibrations and shocks encountered during handling, transport and use in portable equipment. The cell must not leak, vent dangerously or ignite.
Additional abuse tests (as applicable)
Depending on the cell design and application, UL 1642 may also require other checks (such as heating tests) to confirm that the cell remains within safe limits even when misused or exposed to abnormal conditions defined by the standard.
Part 5. Why is UL 1642 certification necessary?
Safety assurance
UL 1642 certification demonstrates that lithium cells have passed a recognized suite of abuse tests. This significantly reduces the risk of field incidents such as fire, explosion or hazardous leakage, especially when cells are integrated into high-volume consumer and industrial products.
Regulatory and standards alignment
While UL 1642 itself is a voluntary standard, many regulatory frameworks, industry specifications and retailer requirements in North America and other regions reference UL or CB-based certifications as part of their safety expectations. Using UL 1642–certified cells helps product manufacturers align with these expectations more easily.
Consumer and OEM confidence
The UL mark is widely recognized and trusted. When OEMs and end users see that cells comply with UL 1642, they have greater confidence that the battery portion of the product has been subjected to independent safety evaluation, supporting purchasing decisions and reducing qualification effort.
Market access and customer requirements
Many brand owners, retailers and distribution channels will only accept products that use cells and packs compliant with appropriate UL standards. UL 1642 certification is often a prerequisite in supply agreements for battery cells destined for high-volume electronics, medical and industrial applications.
Brand protection and risk mitigation
Using UL 1642–certified cells helps manufacturers reduce the likelihood of safety-related recalls, liability claims and damage to brand reputation. If an incident does occur, being able to show that recognized safety standards were followed is an important part of demonstrating due diligence.
International acceptance
Although UL is a North American organization, UL 1642 is widely recognized globally and often used alongside IEC and UN standards (such as IEC 62133 and UN 38.3). This makes UL 1642 certification a strong building block for companies looking to sell lithium battery products into multiple international markets.
Part 6. FAQs
What is the difference between UL 2054 and UL 1642?
UL 1642 applies to individual lithium cells and batteries, focusing on the cell-level safety of lithium chemistries under mechanical, electrical and thermal abuse. UL 2054, by contrast, applies to complete household and commercial battery packs (which may contain lithium, NiMH, alkaline, etc.) and evaluates the safety of the entire pack, including enclosure, wiring, protections and multiple cells working together. In practice, many packs are built from UL 1642–compliant cells and then certified as a pack to UL 2054 (or another pack standard).
What is the difference between UL 1642 and IEC 62133?
UL 1642 is a UL (North American) safety standard focused on lithium cells and batteries. IEC 62133 is an international IEC safety standard for portable sealed secondary cells and batteries with alkaline or other non-acid electrolytes, covering both nickel systems (NiMH, NiCd – IEC 62133-1) and lithium systems (IEC 62133-2). UL 1642 is cell-focused and lithium-only; IEC 62133 is broader in chemistry scope and is commonly used as a basis for CB Scheme and global approvals of portable rechargeable batteries.
What is the UL 1973 standard?
UL 1973 is a safety standard for batteries used in stationary and motive auxiliary applications, such as energy storage systems (ESS), UPS, telecom backup, and certain rail or industrial vehicles. It covers rechargeable battery systems used for stationary energy storage and for on-board auxiliary power, but not the main traction batteries of electric vehicles (which are typically covered by UL 2580 or other EV-specific standards).
What is the IEC code for batteries?
There is no single IEC code that covers all batteries. Instead, the IEC publishes a family of battery standards. Common examples include:
- IEC 60086 series – primary (non-rechargeable) batteries
- IEC 61960 – secondary lithium cells and batteries for portable applications (performance)
- IEC 62133-1 / 62133-2 – safety of portable sealed secondary nickel and lithium systems
Different chemistries and applications use different IEC standards, so the applicable “code” depends on the battery type and use case.
Is UL 1642 mandatory?
UL 1642 is not a law by itself, so it is not universally mandatory. However, compliance with UL 1642 (or equivalent) is often required by OEM customers, retailers, certification bodies and insurance or regulatory frameworks, especially for products sold in North America. Using UL 1642–certified cells is a practical way to meet market expectations for lithium cell safety and to support overall product compliance and risk management.