CE Battery: Ensuring Safety and Compliance in Energy Storage Solutions
As renewable energy adoption accelerates worldwide, the demand for reliable energy storage systems—especially lithium-based batteries—continues to grow. Among the key requirements for these products is CE compliance, a mandatory conformity mark for batteries sold within the European Economic Area. Understanding CE requirements is essential for manufacturers, distributors, and system integrators to ensure both safety and regulatory compliance.
This article explains what CE compliance means for batteries, why it is important for energy storage applications, and the core regulations that govern battery products in the European market.
Part 1. What is a CE battery?
A CE-marked battery is one that conforms to the European Union’s Conformité Européenne (CE) requirements, demonstrating that the product meets all applicable EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards. For battery manufacturers, this marking signifies compliance with relevant directives and harmonized standards—such as the Low Voltage Directive (LVD), the EMC Directive, and, where applicable, the Battery Regulation (EU 2023/1542).
For consumers and system integrators, the CE mark provides assurance that the battery has been evaluated through appropriate conformity assessment procedures and meets the minimum regulatory requirements necessary for safe use within the European market.
Types of Batteries Requiring CE Marking
CE marking applies to a broad range of battery chemistries and formats that are placed on the European market. The most common categories include:
• Lithium-ion batteries – Widely used in consumer electronics, energy storage systems, electric mobility solutions, and industrial equipment.
• Lead-acid batteries – Common in automotive starting batteries, backup power systems, and industrial applications.
• Nickel-cadmium (Ni-Cd) batteries – Typically found in power tools, emergency lighting, and specialized industrial systems where high durability and temperature tolerance are required.
It is important to note that CE marking does not depend on chemistry alone; it applies when a battery falls under specific EU directives or regulations—particularly the new Battery Regulation (EU 2023/1542), which governs all batteries sold in the EU.
Why CE Marking Is Important
CE marking plays a critical role in the European battery market and offers several key benefits:
1. Ensures Product Safety
CE compliance requires manufacturers to meet essential safety requirements, reducing the risk of hazards such as thermal runaway, electrical failure, or leakage. This is fundamental for user protection, especially for high-energy lithium-ion batteries.
2. Enables Legal Market Access
CE marking is mandatory for placing most battery products on the EU market. Without it, products can be rejected at customs, restricted from sale, or subject to penalties. For manufacturers and exporters, CE compliance ensures smooth entry into the European Economic Area.
3. Supports Environmental and Sustainability Standards
With the introduction of the EU Battery Regulation, CE-compliant batteries must also meet environmental requirements related to material sourcing, carbon footprint declaration (for certain categories), recycling efficiency, and end-of-life management. This helps promote responsible manufacturing and sustainable battery lifecycles.
Part 2. The role of CE batteries in energy storage solutions
CE-compliant batteries play an essential role in modern energy storage systems, supporting the efficient use and distribution of renewable energy. Their importance can be understood through several key functions:
1. Improving Energy Efficiency
CE-marked batteries help capture surplus energy generated during periods of high renewable output—such as midday solar peaks or strong wind conditions. This stored energy can then be discharged during times of low production or increased demand, reducing dependence on conventional fossil-fuel power sources and improving the overall efficiency of the energy system.
2. Enhancing Grid Stability
As renewable penetration increases, energy supply becomes more variable. CE-compliant batteries contribute to grid stability by providing fast-response power, supporting voltage and frequency regulation, and mitigating fluctuations caused by intermittent energy generation. These capabilities are critical for maintaining a reliable and resilient grid as more renewable resources are integrated.
3. Enabling Effective Integration of Renewable Energy
Lithium-based energy storage systems—when properly certified and CE-compliant—allow renewable energy assets such as solar PV and wind turbines to operate more efficiently. By storing excess generation and delivering it when needed, these systems help maximize renewable utilization, reduce curtailment, and lower greenhouse gas emissions. This makes CE-compliant batteries a foundational component in modern renewable energy projects and sustainable grid infrastructure.
Part 3. CE battery products requiring CE certification
A wide range of products rely on batteries that must comply with CE requirements to ensure safety, electromagnetic compatibility, and environmental standards. Key product categories include:
1. Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Electric vehicles depend on CE-marked high-voltage battery systems for traction, energy storage, and overall operational efficiency. Compliance ensures that the battery pack meets essential safety and environmental requirements applicable to the European market.
2. Portable Electronic Devices
Devices such as smartphones, laptops, tablets, wearables, and other consumer electronics typically use lithium-ion cells or packs that require CE conformity. This marking confirms that the battery meets the necessary standards for electrical safety, EMC, and chemical compliance.
3. Energy Storage Systems (ESS)
Residential, commercial, and industrial ESS—especially those paired with solar PV or wind generation—must incorporate CE-compliant battery modules and battery management systems. CE conformity helps ensure safe installation, reliable operation, and regulatory compliance under the EU Battery Regulation and related directives.
4. Cordless Power Tools
Rechargeable battery packs used in cordless drills, saws, grinders, and other power tools must meet CE marking requirements. These include electrical safety, mechanical robustness, and EMC performance, ensuring that the tools operate safely across various working conditions.
Part 4. Safety standards for CE batteries
Safety is a fundamental requirement for any battery placed on the European market, and CE compliance incorporates several key international standards. The following safety standards are among the most relevant for batteries used in consumer, industrial, and energy-storage applications:
IEC 62133 — Safety Requirements for Portable Rechargeable Cells and Batteries
IEC 62133 is one of the most widely recognized international standards for the safety of portable sealed secondary cells, particularly lithium-ion and nickel-based chemistries. It focuses on preventing electrical and mechanical hazards throughout the battery’s intended use.
Key safety aspects include:
• Mechanical Safety
Ensures that cells and battery packs can withstand shock, vibration, impact, and other physical stresses without leakage, venting, rupture, or thermal events.
• Electrical Safety
Assesses risks such as overcharging, external short circuits, forced discharging, and incorrect charging conditions. Proper protection circuitry and BMS functionality are critical components of compliance.
IEC 62133 is commonly required for CE marking when batteries fall under the Low Voltage Directive or other applicable EU regulations.
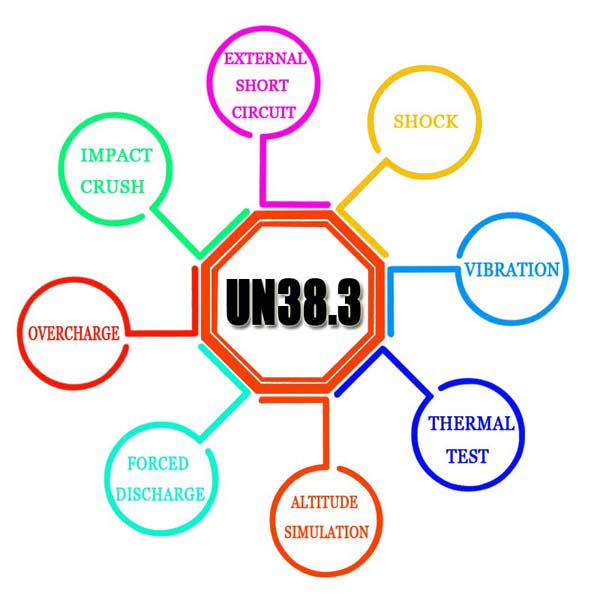
UN 38.3 — Transport Safety for Lithium Batteries
UN 38.3 is not a CE standard, but it is mandatory for all lithium cells and batteries transported by air, sea, rail, or road. This regulation ensures that batteries can safely endure the stresses of global logistics.
Key tests include:
• Altitude Simulation (T1)
Verifies cell and battery integrity under low-pressure conditions encountered during air transport.
• Thermal Cycling (T2)
Evaluates the ability of the battery to withstand repeated extreme temperature variations without venting, leakage, or structural failure.
UN 38.3 compliance is required before lithium batteries can be shipped internationally, regardless of destination market.
Part 5. CE battery testing and certification processes
To obtain CE marking, manufacturers must ensure that their batteries comply with all applicable EU directives and the Battery Regulation (EU 2023/1542). This process involves structured testing, technical documentation, and conformity assessment procedures. The key components include:
1. Product Testing
Manufacturers must conduct a comprehensive series of tests to verify the electrical, mechanical, and environmental performance of the battery. Typical evaluations include:
• Capacity Testing
Measures the battery’s nominal capacity and verifies that it performs within the declared specifications.
• Cycle Life Testing
Assesses the number of charge–discharge cycles the battery can sustain before its capacity falls below the defined threshold. This test helps validate durability and long-term reliability.
• Safety and Abuse Testing
Depending on the battery chemistry and application, additional tests may include overcharge protection, short-circuit behavior, thermal stability, vibration resistance, and other safety-critical evaluations.
While CE marking does not mandate a fixed test list, manufacturers typically reference harmonized standards such as IEC 62133, the Low Voltage Directive (if applicable), and EMC requirements.
2. Technical Documentation Requirements
To demonstrate compliance, manufacturers must create and maintain a complete technical file. This documentation must be available to EU authorities upon request and typically includes:
• Technical File
A detailed compilation covering design drawings, component specifications, manufacturing processes, BMS description, wiring diagrams, labeling, intended use, and performance data.
• Risk Assessment
A systematic analysis identifying potential hazards such as electrical, mechanical, chemical, or thermal risks, along with mitigation measures implemented during design and production.
• Test Reports and Compliance Evidence
Documentation proving that the product meets relevant EU directives and standards.
This documentation is a core element of the CE conformity assessment process.
3. Conformity Assessment — Manufacturer or Notified Body (Depending on Category)
For most battery types, manufacturers may complete CE conformity through self-declaration, provided they have met all applicable requirements and compiled the required technical documentation.
However, under certain conditions—such as specific categories defined in the EU Battery Regulation or equipment that falls under directives requiring third-party involvement—a Notified Body may be required to perform part of the conformity assessment.
A Notified Body:
- Reviews the manufacturer’s technical file
- Evaluates testing and compliance evidence
- Confirms adherence to applicable EU regulations
This adds an additional layer of verification for higher-risk products.
Part 6. Common applications of CE batteries
CE-compliant batteries are used across a wide range of modern applications, highlighting their versatility and critical role in today’s energy landscape. Key application areas include:
1. Electric Vehicles (EVs)
In electric mobility, CE-compliant battery packs supply the energy required for traction, on-board electronics, and regenerative braking systems. Compliance ensures that high-voltage lithium battery systems meet essential safety, EMC, and environmental standards required within the European market. This contributes to both vehicle performance and user safety.
2. Renewable Energy Storage Systems
In solar and wind installations, CE-marked energy storage systems allow excess energy produced during peak generation hours to be stored and delivered when production drops. This capability improves energy availability, enhances system reliability, and supports the broader integration of renewables into the grid.
3. Consumer Electronics
CE-compliant lithium-ion batteries power a vast array of consumer devices—including smartphones, laptops, tablets, wearables, and handheld tools. Compliance ensures these batteries meet the necessary safety, chemical, and EMC requirements for everyday use, reducing risks such as overheating or electrical faults.
4. Power Backup and UPS Systems
Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), telecom backup systems, and critical infrastructure rely on CE-compliant batteries to deliver stable backup power during outages. These applications require batteries that meet stringent safety and reliability standards to support continuous operation.
Part 7. Challenges facing CE battery compliance
Although CE-compliant batteries offer significant advantages in safety, reliability, and market access, manufacturers still face several challenges when meeting regulatory requirements.
Key Challenges in Achieving CE Compliance
1. Rapid Technological Advances
Battery technology evolves quickly—whether in cell chemistry, BMS design, energy density, or thermal management. This pace of innovation can make it challenging for manufacturers to continuously align their products with updated EU directives, harmonized standards, and the new requirements introduced by the EU Battery Regulation (EU 2023/1542).
2. Cost of Compliance
Meeting CE marking requirements can be costly, particularly for small and medium-sized manufacturers. Expenses may include:
- Laboratory testing (electrical, mechanical, EMC, chemical compliance)
- Product redesign to address non-conformities
- Technical documentation preparation
- Conformity assessment fees (including potential Notified Body involvement)
While these costs are essential for ensuring product safety and legal market access, they remain a significant barrier for some manufacturers.
Best Practices for Manufacturers
To effectively navigate CE compliance and reduce the risk of delays, redesigns, or regulatory issues, manufacturers should adopt the following practices:
1. Stay Updated on Regulatory Requirements
Regulations and standards evolve regularly. Manufacturers should:
- Monitor updates to EU directives and the Battery Regulation
- Participate in industry associations and technical committees
- Maintain communication with regulatory authorities and certification bodies
Proactive awareness ensures that product design and development remain aligned with current compliance expectations.
2. Invest in Robust Quality Assurance Systems
A strong quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC) framework is essential. This includes:
- Incoming material inspections
- Process control during cell and pack assembly
- End-of-line electrical and safety testing
- Traceability systems
- Regular audits of suppliers and manufacturing lines
A well-managed QA system reduces defect rates, minimizes compliance risks, and enhances long-term product reliability.
3. Engage with Notified Bodies Early in the Process
For battery categories that require third-party involvement, collaborating with a Notified Body early in the development cycle is highly beneficial. Early engagement helps:
- Identify potential non-compliance issues before mass production
- Clarify applicable standards and test requirements
- Streamline the overall CE conformity assessment
- Avoid costly redesigns or delays later in the process
Part 8. FAQs
What does CE marking mean for batteries?
CE marking indicates that a battery meets the European Union’s essential safety, health, and environmental protection requirements. It shows that the product has undergone appropriate conformity assessment and is safe for use within the EU market.
How do CE-compliant batteries support renewable energy?
CE-compliant batteries store surplus energy generated from renewable sources such as solar and wind. By releasing this stored energy during periods of low production, they help balance supply and demand, improve grid reliability, and reduce dependence on fossil-fuel power generation.
What are the key safety standards for batteries requiring CE conformity?
Important standards include IEC 62133, which defines electrical and mechanical safety requirements for portable rechargeable batteries, and UN 38.3, which sets mandatory transport safety tests for all lithium batteries. Although UN 38.3 is not a CE standard, it is required for international shipping.
Which regulations govern the use of batteries in the EU?
The primary regulatory framework is the Battery Regulation (EU 2023/1542), which replaces the older Battery Directive (2006/66/EC). It establishes requirements for design, safety, labeling, sustainability, and end-of-life management. The RoHS Directive (2011/65/EU) also applies to batteries used in electrical and electronic equipment by restricting hazardous substances.
What challenges do manufacturers face in achieving CE battery compliance?
Manufacturers often face challenges such as rapidly evolving battery technologies, the cost of testing and documentation, and the ongoing need to monitor regulatory updates. Maintaining strong quality assurance systems and staying informed about new standards are essential for long-term compliance.